For more than three decades, insurance organizations have turned to automation to solve operational challenges. Robotic process automation (RPA), business rules engines, and macros have all delivered incremental improvements in speed and consistency. They helped reduce keystrokes, cut down on rekeying errors, and allowed teams to process larger workloads without expanding headcount.
Yet, as insurers now confront surging customer expectations, heightened regulatory scrutiny, and a workforce shortage projected to reach hundreds of thousands with retirements by 2026, static automation is no longer enough. The insurance industry must move from simply automating tasks to deploying artificial intelligence (AI) that can reason, learn, and adapt.
Let’s look at the key differences between static automation and AI, why insurers need to make the shift, and how they can do so responsibly while safeguarding compliance, profitability, and customer trust.
Moving Automation Beyond RPA, Business Rules, Macros, and Templates
Traditional automation in insurance has largely been “static.” By static, we mean systems that follow rigid, predefined rules.
- Robotic process automation (RPA): Mimics human keystrokes or clicks to move data between systems. Useful for high-volume, repetitive tasks but brittle when formats or processes change.
- Business rules engines: Encodes underwriting or claims rules into “if/then” logic. Effective for consistency but limited when exceptions or new patterns emerge.
- Macros and templates: Save time on repetitive communications or forms but add little value beyond efficiency.
These tools provide stability but lack flexibility. They cannot understand context, interpret unstructured documents, or adjust when data or conditions evolve.
AI, on the other hand, introduces adaptive capabilities. AI can classify submissions, extract data from ACORD forms, detect fraud patterns, and even converse with policyholders. Unlike static automation, AI is not locked to a set of rules. It learns from historical data, improves with feedback, and continues to adapt as new information flows in, while creating efficiencies and providing quicker service to your customers.

Your Insurance AI Transformation Can’t Wait
Across the insurance landscape, the ground is shifting. Customer needs, talent market realities, and regulatory demands are converging to make AI-powered automation not just an advantage – but a necessity.
1. Customer Expectations
Policyholders and brokers now expect insurance to operate at the speed of Amazon, Apple, or their bank. Static automation can shave seconds off repetitive tasks, but it cannot deliver the real-time responsiveness required to compete in a digital marketplace. AI can.
2. Workforce Pressures
The insurance industry is experiencing a longstanding talent shortage. Many seasoned underwriters and claims adjusters are retiring, and fewer new professionals are entering the field. Static automation does not scale knowledge. AI, however, can capture expertise, standardize decision-making, and free employees to focus on higher-value activities like risk analysis and customer relationships.
3. Competitive Pressures
Static automation provides parity at best. Most carriers can implement the same macros or RPA bots. AI, by contrast, offers differentiation. A carrier that deploys AI for underwriting intake, claims indexing, or fraud detection can quote faster, resolve claims sooner, reduce leakage, and provide a superior customer experience, all of which build competitive advantage.
4. Compliance and Risk Management
Regulators are increasingly focused on transparency and data protection. Static automation follows the same path every single time, without deviation. AI, when implemented responsibly, can provide greater transparency via robust audit trails to demonstrate regulatory compliance.
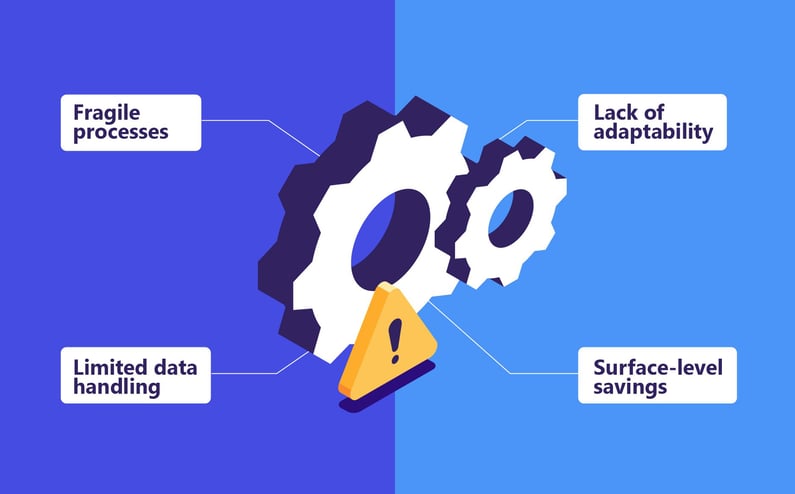
Static Automation Falls Short in Today’s Data-Intensive Insurance Workflows
To understand the case for shifting, it helps to see where static automation breaks down:
- Fragile processes: A single change in a PDF template or claims form can break an RPA bot, meaning that entire systems stop while the bot is out of service.
- Limited data handling: Rules engines struggle with unstructured documents like medical records, police reports, or photos. For example, static automation cannot tell when the same event date is presented in two different format, requiring human review.
- Lack of adaptability: When market conditions shift, for example during catastrophe events or regulatory changes, static automation cannot adjust without manual reprogramming.
- Surface-level savings: Automating a few keystrokes or email templates saves time but does not fundamentally reduce cost or expand capacity.
These limitations mean insurers that rely only on static automation are stuck with incremental efficiency gains rather than transformative change.

The Advantages of Insurance AI Over Traditional Automation
Conventional automation methods and tools can only take insurers so far. Here are some of the ways AI introduces a new level of understanding, learning, and flexibility to making automation not only faster, but fundamentally more intelligent.
- Understands Unstructured Data
AI excels at extracting meaning from unstructured inputs. Combining optical character recognition (OCR), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision enables AI-powered solutions to accurately process a wide range of insurance forms and documents. - Continuously Learns
AI models improve as they process more data. Unlike static automation, which requires human intervention to update rules, AI adapts automatically. This makes it more resilient to different versions of forms, submission response formats, or regulatory adjustments. - Human-in-the-Loop Support
AI is not designed to replace human expertise but to augment it. AI agents can handle 80 to 90 percent of routine intake and routing, while underwriters or adjusters review exceptions. This partnership accelerates throughput while maintaining quality and compliance. - Scalability and Flexibility
AI enables insurers to scale up or down rapidly. During January 1 renewal season or after a natural disaster, AI can expand capacity instantly, absorbing surges in volume without requiring proportional increases in staff or overtime. - Advanced Risk Detection
AI can identify anomalies that static systems miss. For example, a rules engine might flag claims based on thresholds, but AI can detect suspicious patterns across thousands of variables, uncovering fraud that would otherwise slip through. - Regulatory Alignment and Explainability
One of the most critical benefits AI delivers is that it can generate audit trails, track decision-making steps, and provide explainability reports that show why a model made a recommendation. This transparency is essential for regulatory compliance and building customer trust that all AI-driven decisions are fair, consistent, and defensible.

How Insurers Can Make the Shift
1. Start with high-impact workflows
Identify processes that are:
- High in volume (loss run processing, FNOL setup, submission triage).
- Highly manual (rekeying, document classification).
- Error-prone or time-sensitive (medical bill indexing, catastrophe claims).
These are ideal candidates for AI-powered digital coworkers.
2. Establish governance early
AI requires stronger governance than static automation. Build governance committees that include IT, compliance, operations, and legal. Document audit trails, create explainability protocols, and ensure human oversight for sensitive workflows.
3. Engage employees
Communicate that AI is a tool to augment staff, not replace them. Train underwriters, adjusters, and service teams on how to work alongside AI. Highlight how AI removes repetitive drudgery and allows them to focus on judgment-driven work.
4. Evaluate vendors carefully
Not all AI vendors are created equal. Insurers should demand proof of:
- Security certifications (i.e., SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, GDPR, CCPA, NYCRR500).
- Insurance expertise (i.e., ability to handle ACORD forms, loss runs, claims data).
- Governance features (i.e., bias audits, explainability, logging).
Choosing vendors with insurance-specific experience reduces risk and accelerates time to value. Public AI tools such as ChatGPT, Copilot, and Gemini are not designed for, or as accurate with, ACORD forms, interpret loss runs, or comply with strict regulatory standards. Relying on them can expose sensitive policyholder data and produce inaccurate results, which is why insurers need partners that bring both technical capability and deep industry expertise.
5. Measure ROI and outcomes
Measure more than just cost savings. Track improvements in accuracy, faster cycle times, and employee satisfaction, and show how AI strengthens profitability, ensures compliance, and enhances customer retention.
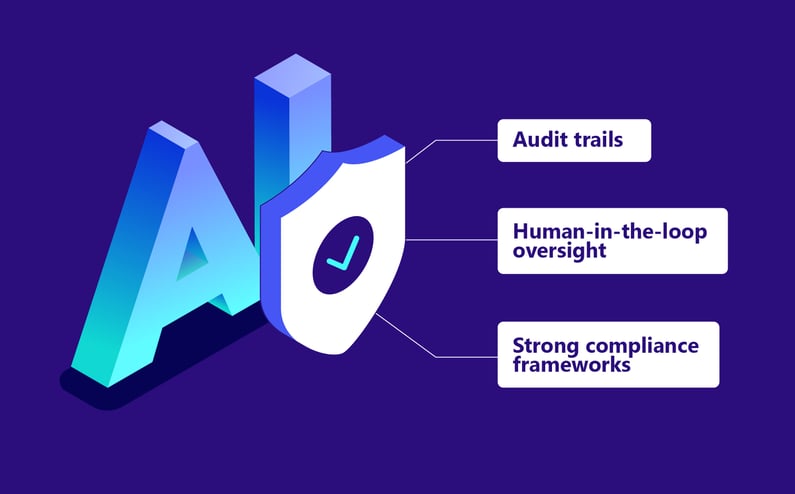
AI Automation for Enhanced Compliance and Efficiency
Some leaders hesitate to move beyond static automation because of perceived risks. Common concerns include:
- Loss of control: Fear that AI will make unexplainable decisions.
- Regulatory exposure: Concern that regulators will scrutinize AI more heavily.
- Employee resistance: Anxiety around the adoption of any new technology.
These concerns are valid but manageable. AI solutions can be designed with explainability and audit trails, human-in-the-loop oversight, and strong compliance frameworks. When implementing AI, including a strong change management plan is essential. Having this prepares employees for new workflows by addressing their concerns and providing training to build confidence. This support fosters adoption by helping team members employees to use AI as a tool for reducing repetitive, low-value work.

Ways Automation Helps Insurance Businesses Attain Their Strategic Goals
The payoff for shifting from static automation to AI is substantial:
- Operational efficiency: AI reduces manual effort by 70 to 90 percent in many workflows.
- Profitability: Faster quoting, claims resolution, and policy servicing improve margins even in low-premium segments like small commercial.
- Compliance readiness: By offering transparency and traceability in decision-making, AI helps insurers meet rising regulatory expectations with confidence.
- Customer experience: Brokers and policyholders receive faster, more accurate service, improving retention and growth.
In short, AI transforms automation from an incremental tool into a strategic driver of competitiveness.
Static automation has delivered value, but it has a ceiling. The next decade belongs to insurers that embrace AI to unlock flexibility, resilience, and intelligence across their operations. Shifting from static automation to AI is not optional. It is the only way to keep pace with customer expectations, talent shortages, and competitive pressures. The question is no longer whether to adopt AI, but how to do it responsibly, securely, and strategically.
This shift is not just about technology. It is about creating space for employees to focus on judgment, service, and relationships while AI handles the repetitive and transactional work. It is about showing regulators, brokers, and policyholders that the industry can innovate responsibly and transparently. And most importantly, it is about delivering the speed and service customers expect today.
There’s an old saying: The best time to plant a tree was 20 years ago. The second-best time is now.
Look closely at the areas where your static automation solutions have reached their limits, or could never even be deployed, and explore how AI can grow your business by adding adaptability and intelligence. Building strong governance around this shift ensures responsible deployment, greater resilience, stronger compliance, and a lasting competitive advantage.
Fast-track your AI business transformation with our guide on How to Navigate Change in the AI-Powered Insurance Future.






